Graph Federated Learning
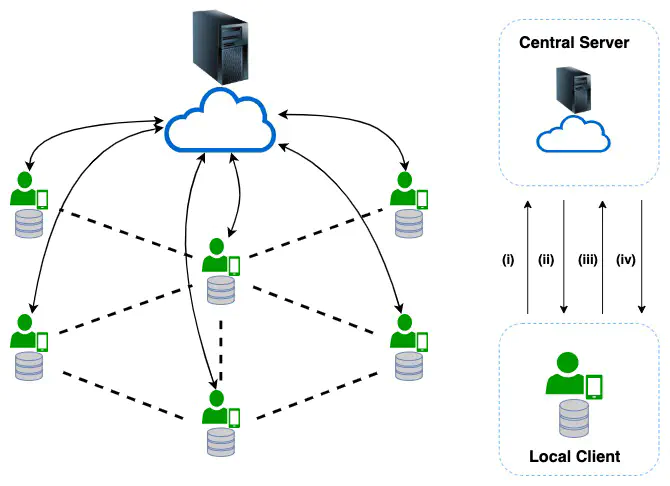
Learning on Graphs (LoG) is widely used in multi-client systems when each client has insufficient local data, and multiple clients have to share their raw data to learn a model of good quality. One scenario is to recommend items to clients with limited historical data and share common preferences with other clients in a social network. On the other hand, due to the increasing demands for the protection of clients’ data privacy, Federated Learning (FL) has been widely adopted: FL requires models to be trained in a multi-client system and restricts sharing of raw data among clients. The underlying potential data-sharing conflict between LoG and FL is under-explored and how to benefit from both sides is a promising problem. In this work, we first formulate the Graph Federated Learning (GFL) problem that unifies LoG and FL in multi-client systems and then propose sharing hidden representation instead of the raw data of neighbors to protect data privacy as a solution. To overcome the biased gradient problem in GFL, we provide a gradient estimation method and its convergence analysis under the non-convex objective. In experiments, we evaluate our method in training graph neural network models of classification tasks. Our experiment shows a good match between our theory and the practice.
More details will be updated by late September.